Read the latest news about research conducted by investigators in the College of Earth and Mineral Sciences. Our faculty and students are continually advancing technology, creating solutions and expanding knowledge with new and innovative research.
News
A multi-institutional research group led by two Penn State faculty members has identified, for the first time, how cellulose crystals orient themselves relative to the cell wall in plants, with potential implications for chemical and energy development.
The measures instituted in April to help curb the spread of COVID-19 across the United States may hold clues for improving air quality, according to researchers.
The effects of climate change are sometimes difficult to grasp, but now a virtual reality forest, created by geographers, can let people walk through a simulated forest of today and see what various futures may hold for the trees.
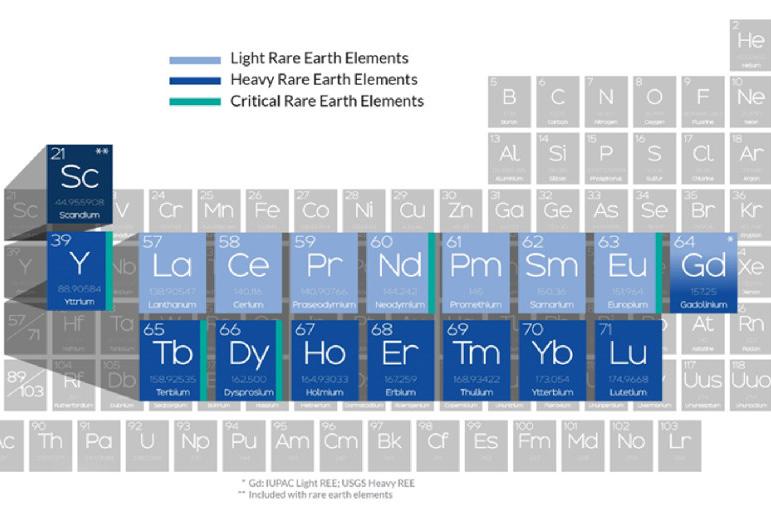
Penn State has entered a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the Colorado School of Mines to establish a collaboration designed to be responsive in supporting the United States’ need for critical minerals.
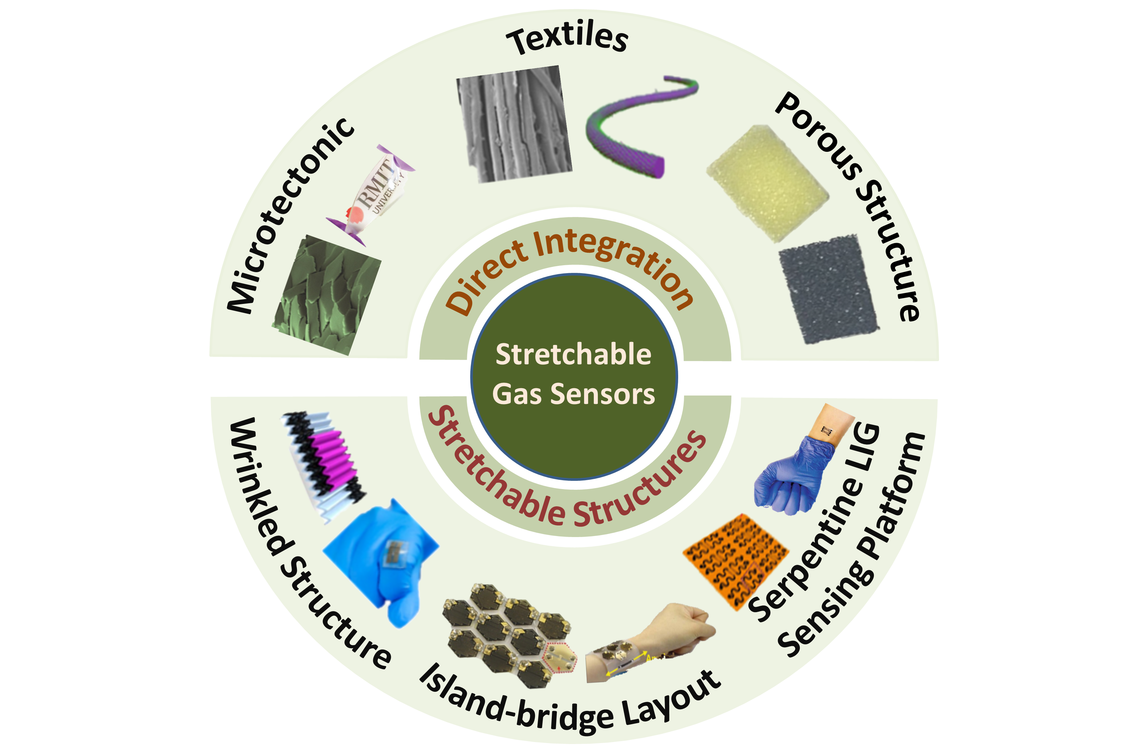
A new understanding of nanomaterials, sensor design and fabrication approaches could help advance stretchable, wearable gas sensors that monitor gaseous biomarkers in humans and toxic gas in an exposed environment, according to Penn State researchers.
A new paper, published by a team of Penn State researchers in ACS Nano, seeks to further advance photodetectors’ use by integrating the technology with durable Gorilla glass, the material used for smart phone screens that is manufactured by Corning Incorporated.
When the Paleocene ended and the Eocene began nearly 56 million years ago, Earth’s atmospheric carbon dioxide levels ranged between 1,400 and 4,000 parts per million (ppm). These carbon dioxide levels gave rise to sauna-like conditions across the planet, which scientists can now measure using tiny minerals called siderites.
A single-step, plasma-enhanced catalytic process to convert sulfur dioxide to pure sulfur from tail gas streams may provide a promising, more environmentally-friendly alternative to current multistage thermal, catalytic and absorptive processes, according to scientists at Penn State.
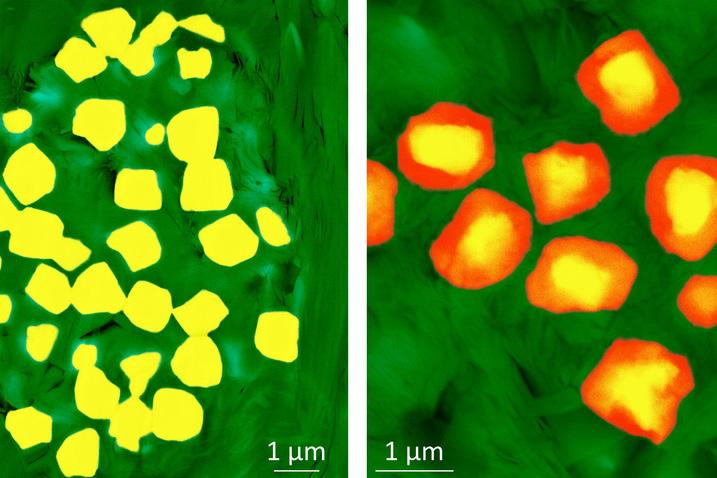
Pyrite, or fool’s gold, is a common mineral that reacts quickly with oxygen when exposed to water or air, such as during mining operations, and can lead to acid mine drainage. Little is known, however, about the oxidation of pyrite in unmined rock deep underground.
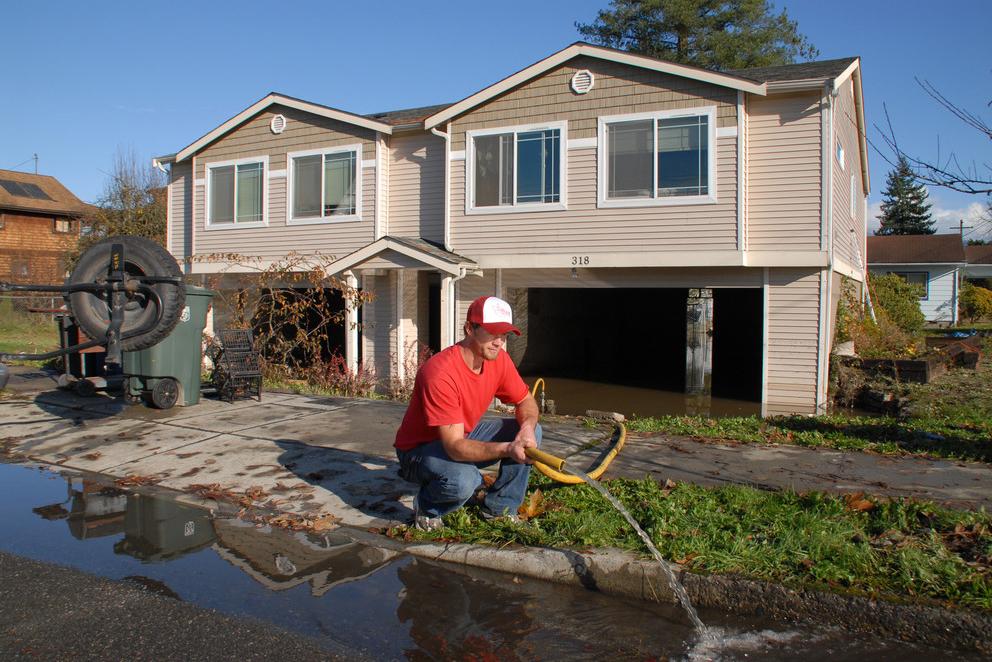
What do you have on your 2020 Bingo Card? Wildfire, heat wave, global pandemic, or flooding? If it’s flooding, then it’s a good bet it will happen in many places in the U.S. sometime during the year.